Long-term results in patients with and without amelogenesis imperfect
Teeth that have been affected by extensive wear or a genetic disorder can be successfully restored with adhesively bonded all-ceramic restorations. The following article summarizes the outcomes of a series of complex clinical cases.
Two different groups of patients require the rehabilitation of impaired full dentitions:
- Patients whose teeth show extensive erosion, abrasion or attrition caused by their diet (e.g. consumption of energy drinks) and/or overuse (e.g. grinding)
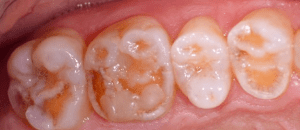
- Patients who have a genetic disorder that affects the tooth structure and the composition of the tooth enamel (e.g. amelogenesis imperfecta, AI) (Figs. 1-3)
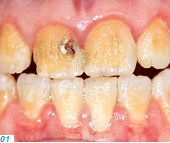
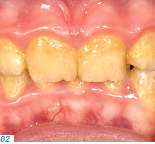
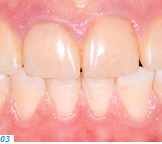
Patients in the first group usually start experiencing problems (e.g. pain and compromised esthetics) in their forties and fifties. The teeth become shorter and look yellowish; parts of the existing tooth structure become fragile and a loss of vertical dimension occurs. Patients with a genetic enamel defect generally require treatment when they are in their teens. Today’s advanced all-ceramic and adhesive systems allow minimally invasive tooth preparation and they produce durable, functional and esthetic restorations.
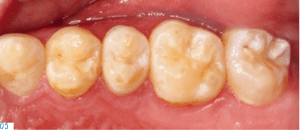
Before treating patients with dental erosion, it is important to obtain their full medical history (e.g. bulimia nervosa or reflux disease) and find out about their eating habits. If possible, their general practitioner should also be involved in the treatment. If the patient is experiencing functional problems, these should be addressed in a pre-treatment phase. In patients with a congenital defect of the tooth structure, a thorough clinical and radiological examination is of utmost importance, since in addition to the enamel defects (Figs. 4-5), these individuals may also suffer from follicular cysts, abnormal tooth eruption, retained or impacted teeth, an open bite or dental pulp calcification (Figs. 6-8).
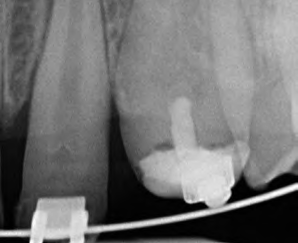
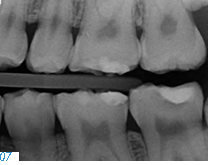
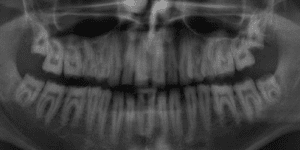
The disorder is furthermore associated with gingival and periodontal disease. This must be taken into consideration in the preliminary treatment of hypomineralized and hypocalcified enamel. Depending on the severity of the impairment of the enamel formation, an adhesive bond may be much weaker than it would be on healthy enamel. As a result, the adhesive bond must be generated in the dentin in most cases (Fig. 9).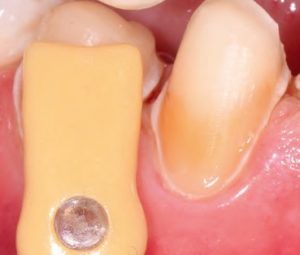
At present, no guidelines or scientific reports of an evidence-based protocol are available for the treatment of patients with AI. In a long-term study conducted at the Tübingen University Hospital, we identified the type of complications which could arise with adhesively placed all-ceramic single-tooth restorations in the mentioned patient groups.
Data Base and Examinations
For our study, we selected patients who regularly attended the recall appointments and who had been treated as follows:
Single-tooth restorations (crowns, partial crowns) made of silicate (Si) or lithium disilicate ceramic (LiDi) had been placed with an adhesive composite.
The patients had lost a maximum of four teeth. The missing teeth were replaced with not more than a three-unit all-ceramic bridge or a single-tooth implant with an all-ceramic crown. The patients whose vertical dimension of occlusal had to be opened by more than 4mm were given an occlusal appliance which they had to wear 24/7 for at least four months before the treatment. The rapid developments in the field of allceramic materials continue to open up new treatment modalities. Initially, however, feldspathic and leucite reinforced silicate ceramics were copy-milled to produce esthetic single crowns, which could be used in posterior teeth and were placed with the adhesive technique.
IPS Empress® II of the first generation of LiDi ceramics reduced the fracture risk due to improved mechanical properties. It was followed by the optimized IPS e.max® Press.
A clinical check-up program was initiated in order to monitor the quality of the treatment results. Therefore, the tooth status, periodontal probing depth and papillary bleeding index as well as the quality of all the restorations were annually assessed and classified according to the Ryge criteria. Irreparable fractures, tooth loss and deep probing depths were classified as “absolute failures.” If the quality of a restoration was deemed to be compromised, but a new restoration was not justified, it was classified as a “relative failure” (e.g. chipping, cracking of the ceramic).
Patients, Observations and Results
The study involved 17 patients between the ages of 12 and 69 (at the time of the restoration placement) and a total of 450 restorations. Nine of the patients suffered from some form of AI. The patients were observed over a period of maximum 17 years. During this time, the following complications occurred in 44 restorations (10 percent) in 11 patients (65 percent): Eleven of the 44 restorations were classified as “absolute failures,” which translates to an overall survival rate of 99.8 percent after three years and 91.4 percent after ten years. No significant differences were noted between patients with or without AI.
Thirty-three of the “relative failures” were caused by chipping. It is interesting to note that 11 of the “chip-offs” were recorded in one patient alone. Despite the observed complications, the success rate was 95.7 percent after three years and 81.4 percent after ten years. A statistically relevant difference was noted between patients with and without AI. The success rate of patients with AI was significantly higher.
Discussion
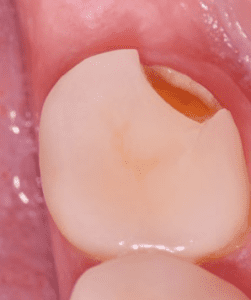
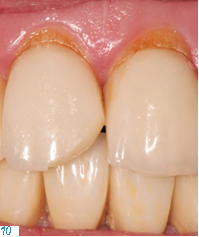
The long-term performance of the different materials was assessed on the basis of adhesively bonded single-tooth restorations. During an observation period of ten years, we found that fractures of single-tooth silicate ceramic restorations were spread over the entire length of time (Figs. 10- 11), whereas lithium disilicate crown failures tended to occur toward the end of it. These results are comparable to those in the literature. Nevertheless, it must be noted that even though the number of
restorations involved in our study was high, the number of patients was relatively low. Consequently, our findings are limited in terms of their validity. They do, however, allow us to identify certain trends.
Molar restorations fractured most frequently: after about five years of service and primarily in patients whose vertical dimension had not been opened. The type of material used may have been responsible for the fractures or the restorations may have been too thin. We were surprised by the fact that the patients with AI had fewer complications than the patients without AI. We had assumed that their restorations would not perform as well due to the “unfavorable” conditions for the adhesive bond. Age may have played a role in this finding, since the patients with AI were about 24 years younger on average compared with the other subjects. In addition, the results of the AI patients showed that adhesive all-ceramic restorations do not cause any endodontic problems. Therefore, they can be classified as a longterm treatment option. Nonetheless, the teeth of patients with AI require circumferential preparation to prevent any weak areas such as cement lines and to restore the function and anatomy of the teeth.
Summary
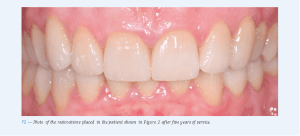
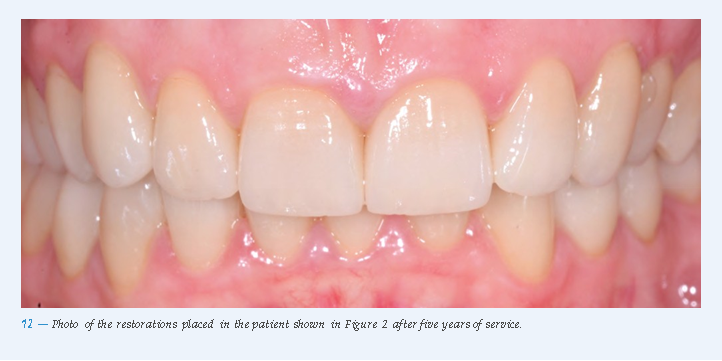
Adhesively cemented all-ceramic single-tooth restorations achieve excellent clinical results irrespective of the initial situation (Fig. 12).Patients with a history of functional problems, however, are expected to have a higher rate of technical complications. Overall, it is likely that about two in one hundred crowns every year will show some sort of complication after five to ten years of service and that primarily restorations in molars will fracture. Therefore, we recommend at least one check-up per year in order to treat any complications as early as possible and therefore minimize the risk of failure.
Annotation
The present results were previously published in the following article: Klink A, Groten M, Huettig F; Complete rehabilitation of compromised full dentitions with adhesively bonded all-ceramic single-tooth restorations: Long-term outcome in patients with and without amelogenesis imperfecta. J Dent. 2018 Mar; 70:51-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2017.12.011. Epub 2017 Dec 21.
The Authors
Dr. Andrea Klink, Dr. Fabian Hüttig and Dr. Martin Groten



Reprinted with permission from the March 2021 Issue of the Journal of Dental Technology







Great article and thank You for Providing Such a Unique and valuable information on dental enamel. you can also check on Crown Dental Care
Thanks for sharing nice info. If you looking for affordable dental restoration services in Florida, Davie, then please visit us.